TKT Core Module 3: Teachers'
and learners' language in the classroom
Categorising learners' mistakes
 |
| Will you tell him or shall I? |
If you have followed the course for Module 1 of the TKT, you already know quite a lot about errors and slips. The TKT syllabus uses the word 'mistake' for both of these but we will make a distinction:
- An error happens when the learners does not know the right language to use.
- A slip happens when the learner is tired or stressed or simply has too much to think about. We all do that in our own languages and it's nothing to worry about.
 |
Key concepts in this guideBy the end of this guide, you should be able to understand and use these key concepts:
|
Look out for these words like this
in the text.
There will be tests at the end of the guide for you to check that
you understand the ideas.
 |
What sorts or errors do learners make? |
Productive or Receptive error |
|
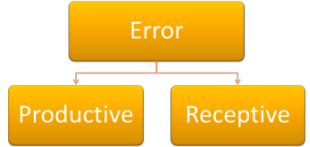 |
When a
learner says or writes something that is wrong, it is easy to
see because it is a productive error. However, if a learner does not properly understand what he or she reads or hears it may not be easy for us to know because it is a receptive error. To find out if there is a receptive error, it is important to test whether understanding has really happened. |
Individual or Group error |
|
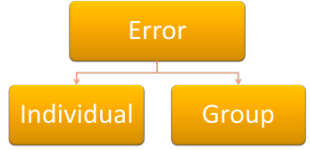 |
If all
or most learners in the class are making the same mistake, it's
called a group error. Group errors are more important than individual errors and call for teaching not just correcting. |
Is it obvious? |
|
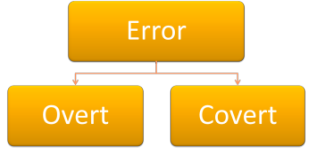 |
Covert errors
occur when, for example, a student says I have been to London – is that right? You can't tell, of course, without finding out what the student actually wants to say. If the learner produces I have been to London yesterday then the error is overt and you can decide whether and how to deal with it. |
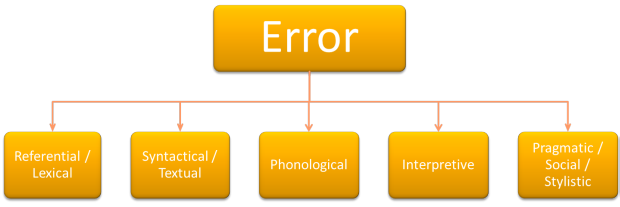
What sort of error is it? |
|
 |
|
- referential or lexical errors
- This simply means that the learner has chosen the wrong word. For example: I opened the pack of chocolate instead of I opened the bar of chocolate.
- syntactical errors
- are sometimes called grammatical errors. It means something is wrong with the structure. For example: He will coming next Thursday. Spelling, form and punctuation errors are also in the category.
- phonological errors
- are, rather obviously, errors in pronunciation. If a learners says I leave in France instead of I live in France (using /liːv/ instead of /lɪv/) we have a phonological error.
- interpretive errors
- are errors in understanding what is meant. For example, if I say Do you have the time? and you reply Yes, thank you., you have not interpreted my meaning clearly (I want to know what time it is now!).
- stylistic errors
- These are sometimes called pragmatic or social errors. If, for example, someone goes to the ticket office and says You, give me a ticket for London! we have a stylistic error because that is unacceptably direct in English (and many languages).
 |
Task 1:
What kinds of errors are these and why do you think they
happened? Think about each one and then click on |
| Error | Type and possible reason |
|
Everyone in my class says What means ... not
What does ... mean? |
|
|
Mary said I go to London on Thursday but she didn't
mean every Thursday, I think |
|
|
He came by boot |
|
|
A: How long are you staying? B: I have been here two hours. |
|
|
It's a big, Chinese, beautiful vase |
|
|
There's a dustbin under the desk. |
|
 |
Skills errors |
Learners can also make mistakes when practising or using skills
but they can usually be categorised in the same ways when they are
receptive errors.
However, not ordering a letter or a report in the right way can be
called a generic error and not being able to get your meaning clear
can be called a communicative error.
 |
Self-test questions |
Before you go on, make sure you can answer these questions. If you can't, go back to the sections which give you trouble.
- Explain the difference between a slip and an error.
- Give an example of a receptive error.
- Explain how you deal with the possibility of covert errors.
- Give an example of a referential error.
- Give an example of a syntactical error.
If you are happy with your progress, go on.
 |
Tests and practice for TKT |
There are two practice tests.
| Test 1 | A matching task |
| Test 2 | What is the error? |
Now you can return to the Module 3 index:
![]()
or go on to the next
guide which is to
classroom management.
