First and Second Language Acquisition Theories

What's the relevance of First Language Acquisition to teaching an additional or second language?
Good question. There are a number of reasons we should know a little about First Language Acquisition (FLA, in the trade):
- It provides a kind of benchmark for theories of Second Language Acquisition (SLA). The theories are parallel in many ways.
- A good deal of methodology in SLA has been premised on the theory that we will acquire a second or additional language in the same way we acquired our first language(s).
- The way the human brain operates in language learning is not radically different (so some theories assert) whether we are learning our first or additional language(s).
At each stage in what follows, we'll be considering how theories of first language acquisition are relevant to teachers of additional languages.
Some Major Theories of First Language Acquisition
 |
Innateness: language is in our genes |
You were not born with the ability to speak, ride a bicycle, play the piano, type, play chess, walk or dive for pearls. What concerns us here are the abilities you naturally develop as opposed to those which you are taught.
Some of this is quite easy. Divide this list into learned
(i.e., taught or self-taught) abilities and those which naturally
develop in all normal children:
Click on the table when you have done that.
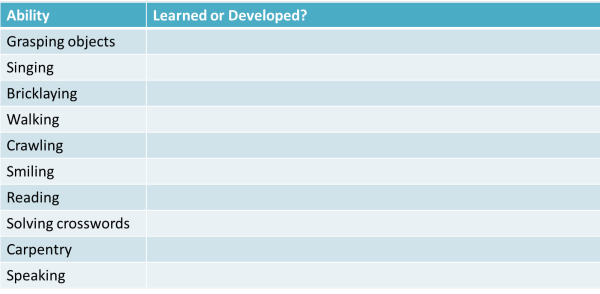
It is clear that some behaviours, such as the ability to grasp
objects or walk are biologically determined because all children,
regardless of their culture, learn to do it pretty much at the same
stage in their development. For example, most babies learn to
sit, then roll over, then crawl and finally walk between the first 9
to 12 months of life (some take a bit longer and some skip the
crawling bit, preferring a bottom shuffle). None, however, has
to be taught the skill.
Babies in all cultures learn to talk between 18 and 28 months of
life.
Some behaviours are never naturally acquired so if you never learn
to ride a bicycle or play a decent game of chess, you will not
magically develop the ability to do so, no matter how long you live.
The question for this guide is whether using language to
communicate is in the same category as walking or the same category
as playing the piano.
This has fairly profound implications but don't expect the
definitive answer here.
biologically controlled behaviours
Aitchison (1989:67 et seq.), drawing on Lenneberg, suggest there are 6
characteristics of biologically determined behaviour. As you
look through the list, ask yourself whether speaking meets each of the
criteria.
Then click on the
![]() to reveal some comments.
to reveal some comments.
| The behaviour
emerges before it is necessary |
Children use language before they need it.
Children are fed, clothed and looked after well into life (sometimes until well after puberty). Children do not need language to survive. What is surprising is that language develops at more or less the same stage in life regardless of the culture. |
| The behaviour
appears without the individual making a conscious decision |
A child does not, it seems clear, suddenly decide to
learn a language.
Individuals may decide to learn other skills, such as bricklaying or playing the flute, but these skills are clearly of a different order from speech. |
| The emergence
of the behaviour is not triggered by external events
(although the environment needs to be sufficiently rich for
it to develop) |
Children begin to talk even when their immediate
environment is unchanging. They live in the same
place with the same people.
The trigger, if there is one, seems to be something internal in the child's development. And that can only be a development in the brain because, physically, there is no reason why a six-month-old baby shouldn't be able to talk perfectly well. On the other hand, however, as the tragic tales of feral children or those brought up isolated from other people demonstrate, language cannot adequately develop without a rich environment with plenty of data for the child's brain to work on. |
| Direct
teaching and intensive practice have relatively little
effect |
If you are learning to lay bricks or play the oboe,
it is quite likely that the amount of teaching and
practice you get will be directly related to your
eventual skills level.
Not so with language, it seems. Although carers often make explicit efforts to correct children's language production, the evidence is that it has almost no measurable effect. The pointlessness of overt correction has been noted by numerous researchers. (Aitchison 1989:69) Practice, too, as we shall see, is not a determining factor in first-language acquisition. |
| There is a
regular series of milestones as the behaviour develops, and
these can usually be correlated with age and other aspects
of development |
All children seem to develop speech in the same way,
reaching certain milestones at approximately the same
age. For example, in English, children develop
word inflexions at around two years of age, and
questions and negatives slightly later. Mature
speech is generally achieved by around 10 years of age.
Moreover, there is a documented and researched order to which items in a language are acquired. For example, in English, it appears that, with minor variations, the progressive -ing structure, the plural -s and articles are acquired before the 3rd person -s, the regular past-tense endings and contracted verbs such as "she's a teacher". |
| There may be a
critical period for the acquisition of the behaviour |
Again, some of the evidence for a critical period
for language acquisition (often cited as between 2 and
13 years of age) comes from tragic cases of brain
damaged or isolated / feral children. In such
cases, it has been noted that language development
proceeds much more slowly and may never result in fully
formed language skills.
This is, you should note, a very controversial area of research and theorising and has been for decades. |
 |
Milestones |
Lending weight to the innateness theory is the often-observed
milestones which all children go through on their journey to fully
competent language use.
The usually cited milestones for first language acquisition are
as follows but evidence is not apparent that the same sequence is
observable in second-language acquisition. There are some
similarities but the parallels are not close.
| Age | Language stage |
| Birth to 3 months | crying, gurgling, non-speech noises |
| 3 to 6 months | babbling |
| 6 to 12 months | intonational babbling |
| 12 to 18 months | words and set phrases |
| 18 to 24 months | increasing vocabulary and rudimentary grammar |
| 24 to 36 months | inflexions and transformations |
| 36 to 60 months | approximation to adult speech patterns |
 |
the evolution of the ability to process languageThere is, unsurprisingly, some debate among evolutionary biologists concerning how such a mechanism may have evolved. Recent genetical research is pointing to a set of genes including one called FOXP2 (pictured). It would be a gross oversimplification to
dub this 'the language gene' as much else, including the
interactions between this gene and a range of others, is involved in
the ability to process language. However, the gene appears to
be central to our ability to process and produce language and people
who lack it or in whom it is mutated or inactive cannot handle
language. |
the U-shaped learning curve
This refers to a phenomenon which has been frequently observed
and researched.
English exhibits a number of irregularities in inflexions, notably
the changing of the middle vowel or consonant to make a past tense form (as in
make-made, buy-bought rather than *maked, buyed
etc.) and in irregular
plurals (such as child-children, mouse-mice etc.)
Children often acquire the irregular form and then revert to an
inaccurate regular form before once more acquiring the irregular
form. So, for example, a child may produce The mice ran up
the clock, then begin to say The mouses runned up the clock
before settling on the correct version later.
If this is true, the importance is obvious: it means that language
cannot be being acquired by simple imitation and practice. If
it were, children would never produce something like *comed
instead of came for the simple reason that they would never
hear it. In other words:
There is not a shred of evidence
supporting a view that progress towards adult norms of grammar
arises merely from practice in overt imitation of adult sentences.
Ervin, (1964:172) cited in Aitchison
(1989:74)
issues
Firstly, while there is strong evidence that some
language-learning ability is innate, a good deal of the theory
has been based on just one language, English. From that,
theorists of universal grammar have averred that the essential
building blocks of language structure are common across all
languages and that these items are what the language acquisition
device is aimed at: noun phrases, verb phrases, adjective
phrases and so on.
This ignores the enormous diversity of structural phenomena
across the range of some 6000 to 7000 languages on earth, many
of which are poorly if at all described. Some, it has been
persuasively demonstrated, get along quite happily without
adjective or adverb phrases at all, for example, choosing to
inflect the noun phrases or verb phrases instead.
Secondly, innateness theories fail, it has been argued, to explain the great differences between spoken and written language. If we are genetically programmed to learn language, whence come these differences?
Thirdly, innateness theories have been criticised as greatly underestimating the effects of culture and community on the language-learning process. In many languages, males and females speak differently and employ different grammatical structures and in some children's language is substantially different from the language of adults. It is difficult to account for these differences on the basis of inheritance of language-learning abilities or pre-programming for language at all.
relevance to (English) language teaching
There are a number of implications for ELT professionals, of course. They come down to the assertion that we should not assume that a second or subsequent language can be acquired using wholly different mental processes from the ones used to acquire one's first language. It is not, after all, as if human mental processes are fundamentally altered in any way as we grow up.
- teaching children
- If the innateness theories are right, then what is required
is simple exposure at the right time to a rich linguistic
environment rather than explicit instruction. Instruction
may, in fact, be counterproductive.
Teachers of children should also bear the acquisition order in mind and not expect or try to demand production of certain forms before the child is 'ready' to learn them.
Practice and correction, too, are pointless. - teaching older children and adults
- Again, if the theories are right, especially concerning the
critical period hypotheses, then we should not expect adults to
acquire language simply by exposure.
We should also expect them never to acquire wholly native-like production if instruction is carried out after the critical period. There is, indeed, some evidence to suggest that in pronunciation especially, older learners never acquire native-like production skills.
The influence of innateness theories is readily seen in some
methodological approaches which rely on rich input and exposure to
language alongside the abjuring of formal practice and instruction.
For more in this area, see the guides to
Krashen and the
Natural Approach and Chomsky, both linked below.
 |
Imitation theory: I speak what I hear |
This theory rests on the fact that children speak the language(s)
in which they were raised. A child taken from an English-speaking
environment at an early age and raised in an Urdu-speaking
environment will acquire Urdu as its first language just as
indigenous children will. The child's genetic background is
wholly irrelevant.
The theory is that imitation must have a role to play because the
connection between a word's sound and form and its meaning is
arbitrary: you cannot infer the meaning of a word from its form so
you must hear it spoken in a clear context to be able to imitate its
use.
Unfortunately,
however, Imitation Theory explains little else of what we know about
language acquisition.
Bergman et al (2007:315)
They go on to explain three major problems with Imitation Theory. From reading what has been said above, what are they? Click here when you have an answer.
- Children's speech is different from adults' speech
Children do not produce fully formed sentences. The evidence is that they progress from 1-word utterances (acquired around 12 months) to 2-word utterances (around 18 months) and then go on to more complex utterances with longer sentences until they start to make rare or complex constructions around 5 years of age.
Indeed, children will often reduce an adult's statement to comply with their current productive capacity. On hearing, for example, something like The train goes through the tunnel an 18-month-old child might reduce it to Tunnel train and an even younger child might reduce it to one imperfectly formed word such as trai'. Children routinely reduce what they hear to conform to their current Mean Length of Utterance or MLU. - The U-shaped learning curve
If imitation were all there was to acquiring language, then the U-shaped curve, going from correct production of irregular forms to overgeneralisation of the rule to recognition of the irregularity (e.g., from went via goed and then back to went) simply would not occur because a child would very rarely, if ever, hear the incorrect form in order to imitate it. Children must, therefore, be actively forming hypotheses about language structure. - Innovation
Both children and adults are capable of forming utterances they have never heard. In fact, the number of possible utterances in a language is infinite. A child might, for example, say Cow river fall even though no adult has ever said it to her. Adults, too, produce language never before heard. For more, see the guide to Chomsky, linked below.
relevance to (English) language teaching
A number of approaches to and techniques in teaching languages
appear to be based on the assumption that people learn language by a
process of imitation of a model.
Behaviourist-based approaches in particular, such as Total Physical
Response, Situational Language Teaching and audiolingualism
emphasise the need for learners to repeat (and be rewarded for)
correct models set in a clear context.
Why do you drill in a classroom if you don't believe imitation and
repetition are
effective?
If the aim is to reflect how a person's first language is acquired
and Imitation Theory is so flawed, then any methodology based on it
will be similarly imperfect.
 |
Reinforcement Theory: praise, correction and reward |
The theory claims that children learn to produce correct language
because they are praised and rewarded (by adult approval) when they
do and are corrected when they don't.
It has, of course, close connections with Imitation Theory (because
correction demands imitation, for one thing) and with behaviourist
theories of learning. Behaviourist theories assert that
learning takes place by the alteration of habitual behaviour. Here's a
very brief summary:

- The process starts with a stimulus, say, a question from a carer such as Who did you see? put to the organism (in this case, a child). The stimulus can elicit a variety of responses but only the 'right' one will be reinforced.
- So, for example, if the child responds with I seed Tom the carer will negatively reinforce it with No, say I saw Tom.
- If, eventually, the carer can persuade the child to produce a correct utterance, the response will be rewarded (i.e., reinforced) with something like Oh! That's lovely! and the child will learn the form.
- Enough Stimulus > Response > Reinforcement cycles will see the habit instilled and the language acquired.
There are three fundamental problems with the
theory. From what has already been said, what are they?
Click here when you have an answer.
- Carers do not focus on form; they focus on content
For example, if a child produces a well formed but untrue statement, carers are more likely to correct it or at least avoid reinforcing it. So a true but incorrectly formed statement may receive praise and a correctly formed but untrue statement will receive censure of some kind. - Cuteness will be reinforced
Carers and other adults have frequently been observed reinforcing false structure and lexical use simply because it is cute and endearing. Thus Choo-choo Bang-bang! while meaningless, uncommunicative and poorly formed may produce a positive response in doting adults. - Even when adults do focus on correcting form, the research
shows that it is almost wholly ineffective. Here's an
example (from Bergman et al, op cit.: 316):
Note that the child is not producing random forms. The child is clearly operating to a rule but the rule differs from the adult's rule and direct attempts at instruction fail.Child: Nobody doesn't like me. Mother: No, say "nobody likes me". Child: Nobody don't like me. (repeated 8 times) Mother (now exasperated): Now listen carefully! Say, "Nobody likes me." Child: Oh! Nobody don't like me.
relevance to (English) language teaching
Much that is recommended in classrooms in terms of praising
learners and error correction is based (even implicitly) on this
kind of behaviourist theorising. It is a short step from
asserting that all learners respond positively to praise and that
praise motivates them to perform better to suggesting that
reinforcing acceptable language will lead to the instilling of
correct language habits.
In other words, a teacher wedded to a cognitivist view of learning
may be using the praise to motivate while one coming from a
behaviourist direction will be using praise to reinforce a response.
You can't tell by watching and it may be the case that the learner
is responding in one way, another way or both ways.
 |
Active Construction of a Grammar Theory |
This theory "holds that children
actually invent the rules of grammar themselves"
Bergman et al (op cit.:316)
The theory is allied to Innateness theory insofar as the ability to
develop rules is presumed innate but the rules themselves will
depend on the structure of the language which children hear around
them.
It has been compared to a kind of switchboard effect which operates
on the data the child hears. So, for example, a French child
will notice that in the language it hears, the adjective normally
follows the noun (un évènement fantastique)
and the switch for noun–adjective ordering will be thrown. A
child in an English-speaking environment will hear, by contrast,
a fantastic event and throw the switch the other way (for an
adjective–noun language). Enough exposure will result in the
switch becoming permanently fixed but French and English children
will still have to be aware of the restriction to the rule in order
to be able to produce un petit problème and the people
responsible correctly.
Such hypothesising about language form neatly explains the U-shaped
learning curve described in this guide. When first acquired,
the rule is applied indiscriminately and then it is later amended to
account for exceptions.
issues
The theory, of course, depends on the assumption that small
children have well developed cognitive abilities and that is by
no means demonstrated by a number of studies. For example,
the ability to recognise that the length of an object is not
dependent on its position or that the volume of a container is
unaffected by its shape are not shown by very young children
(and indeed by all adults).
The fact, too, that all children seem to develop language in
more or less the same stages at the same ages would lead one to
believe that all children everywhere and in all environments
have exactly the same cognitive ability to form
and amend hypotheses about language as they hear it spoken
around them. That is not borne out by the data.
relevance to (English) language teaching
If learners (of whatever age) of a second or subsequent language are applying this kind of cognitive rule-forming behaviour to the language they encounter then concepts such as noticing and the positive role of error in the refinement of language theory in the minds of learners become even more important. See the guides to noticing and to error, both linked below in the table of related guides, for more.
 |
Connectionist Theory |
We'll take a problem for the Active Construction of Grammar
Theory as the starting point. That theory explains the
production of false items such as feets, He showeds me
or mouses as evidence that learner is making
overgeneralisations from rules imperfectly acquired in terms of
their restrictions.
Anecdotally, you may be able to think of the same phenomenon
occurring with learners of English as an additional or second
language.
However, when children are asked to make past tenses or plurals from
nonsense words which resemble real but irregular forms, they do not,
apparently, apply the grammar rules but respond in terms of
statistical likelihood!
For example (again, from Bergman et al), when asked to form
the past tense of fring, many children will suggest
frang or frought (by analogy with ring and
bring etc. respectively) rather than the structurally
predictable fringed.
Hence, too, one might encounter a suggestion that the plural of
frouse would (or might well) be frice not frouses
and it is true
that many native speakers of English will prefer handkerchieves
as the plural of handkerchief by analogy with
wolf-wolves etc. and the status of roof-roofs/rooves
is unclear.
It has been suggested here that humans make neural connections in
the brain based on the frequency of what they hear rather than
making rules based on the structure of what they hear.
statistical reasoning

Another way to explain this process is to rely on inferencing (to which there is a dedicated guide on this site, linked below). It works like this:
If you are presented with the names of six horses in a race and
no other data at all, you would be correct in thinking that your
chances of backing the winner are 6:1 against, i.e., a roughly
16.67% chance that you would win.
However, if you are also told that of the six horses only number 5
has ever won a race before against similar opposition and that all
the others have finished last or second to last in their previous 3
races, you might adjust your expectation of which horse will win
based not on intuition or guesswork but on the statistical
probabilities the new data have supplied.
The theory is that human learning happens like that.
Now take the situation in which you are faced with trying to
decide what form of a verb will follow the verb arrange in
a sentence such as
I arranged __________ tomorrow
and the choices are:
going
go
will go
to go
goes
went
All things being equal, you might think that you have a one-in-six
chance of hitting on the right form. However, all things are
not equal because you already know that the following sentences are
correctly formed:
I hope to go
I agreed to go
I asked to go
I decided to go
I remember going
I recall going
I enjoyed going
The reasoning (which is mostly unconscious) goes like this:
- In all the correct forms I know, none takes the bare infinitive, the present with -s, the will + infinitive structure or the past tense so I can dismiss all those for the moment.
- I now have a choice between to go or going as the correct form. Shall I toss a coin to decide?
- No. I also know that all the forms with -ing that I know are correct are concerned with the past so going comes before the remembering, recalling and enjoying.
- However, I can also see that the forms I know that are correctly formed with a to-infinitive work the opposite way around so the hoping, agreeing, asking and deciding all come before the next action.
- Statistically, therefore, I will select:
I arranged to go tomorrow
and you'll be right, of course.
What you have done is apply probabilistic reasoning based on
your other knowledge of the language and assumed that, statistically
speaking, you'll be right to bet on the favourite.
Just as in horse races, of course, this will not always result in a
win (or bookmakers would all be out of business). If you apply
the same process to a sentences such as:
I look forward ____________ tomorrow
you will not get the right answer. An outsider has won the
race, in this case.
Dennett, 2017:269, puts it this way:
... the brain's strategy is continuously to create "forward models," or probabilistic anticipations, and use the incoming signals to to prune them for accuracy – if needed. When the organism is on a roll, in deeply familiar territory, the inbound corrections diminish to a trickle and the brain's guesses, unchallenged, give it a head start on what to do next.
What we do next, of course, is understand and, if necessary, act on the linguistic data we are receiving.
It may also be the case that both Connectionist and Active Construction of Grammar strategies are being deployed simultaneously.
issues
There are those who consider that the connectionist view of
language acquisition adds nothing substantial to the theory of
active construction of grammar. What it does is add
another layer of cognitive processing and there is nothing
within active construction theory that denies that.
The fact that all languages contain many examples of
non-intuitive and exceptional structures also presents problems
for the theory. We might assume, following the statistical
analogy approach, that all of the following are, for example,
allowable but children rarely, if ever, produce such forms.
If the brain is indeed forward modelling from data it already
has, why is that?
unsage (by analogy with unwise)
I look forward to see you (by analogy with I
want to see you)
I concealed behind the door (by analogy with I
hid behind the door)
I suggested to go out (by analogy with I
expected to go out)
However, the fact that adult learners do produce such forms
consistently provides some evidence that the connectionist view
has more relevance to the teaching of languages to adults and
the existence of analogy errors has long been accepted.
relevance to (English) language teaching
If the two approaches are being combined, in fact, by mature learners as well as children, there are some implications especially for how language is presented and which language is selected for presentation.
- Connectionist theories clearly have a good fit with approaches such as The Lexical Approach and focuses on collocation and colligation. If it is true that learners (of whatever age) are applying some kind of statistical analysis to the language data they are exposed to, then it makes sense to design materials which contain statistically likely rather than unlikely combinations of words and structures.
- Chunking of language, too, is important because chunks such as air conditioning + unit, steering + committee / wheel etc. lend themselves to the formation of neural pathways in the brain.
- Getting learners to notice connections in terms of colligation will also be effective if connectionist theories hold water. The acquisition of, e.g., I allowed him to go, Mary permitted him to come, I forbade him to speak etc. will be facilitated if they are presented together and frequently encountered but presenting them alongside I made him go, I let him speak etc. will be positively counterproductive. The same consideration would apply to all compare-and-contrast rather than notice-the-similarity approaches.
 |
Social Interaction / Constructionist Theory |
This theory places great emphasis on the kinds of social
interaction in which people encounter language. The argument
is that it may be combined with both Connectionist and Active
Construction of Grammar theories to explain how the richness, or
otherwise, of the data the learners encounter will be exploited.
It seeks also to explain how it is that children slowly develop the
ability not only to use language accurately but also appropriately.
Theoreticians in this area focus a good deal of attention on what is
called child-directed speech. Such speech tends to be
delivered with excessive intonation range and pitch and to be
simplified and repeated for comprehension. From it, the child
learns to de-code its meaning before going on to be able to
comprehend and produce more complex and appropriate adult-to-adult
language.
issues
While interesting, there is little actual evidence that the
theory is sustainable. Intuitively, one might consider
that social interaction is vital for the development of
appropriate language use but that can also be explained by the
direct correction of children by adults when they produce
inappropriate language and by imitation theory.
That exposure to language in use is required for language
acquisition has never been in doubt. What role the nature
of the interactions between children and carers plays in the
acquisition of language is.
relevance to (English) language teaching
In terms of second-language acquisition, the theory states
that learning is constructed by the learners. This is
usually contrasted in educational theory with what is labelled
as a transmission model in which knowledge is handed down from
above.
The criticism of that is, naturally, that social constructivists
are setting up an unrealistic 'traditional' model in order to
suggest how social constructivism is superior.
It is, moreover, asserted that learning is primarily a social
activity. This means that knowledge and skills are not
acquired by individuals operating alone but only through
interaction with others.
This makes the theory a good fit with communicative classroom
approaches which forefront real communicative tasks and
emphasise interaction with peers and others.
Clearly, much of Communicative Language Teaching lays great stress on natural and appropriate language as the target of instruction and this theory sits well with such an approach. The procedure of introducing simplified language and then refining it for appropriate and accurate communicative effect lies at the heart of such an approach.
It has sometimes been a criticism levelled at a communicative
approaches to language teaching that while the approach has a
well worked out theory of language, it is less certain about a
theory of learning. Enter social constructivism to the
rescue.
Unfortunately, the theory is somewhat silent concerning the
mechanisms through which learning takes place (unlike, e.g.,
connectionist and active construction theories). It may,
therefore, be wise to reserve judgement or, at least, to take
the view that while social interaction is undoubtedly a useful
and motivating factor in second-language acquisition, it cannot
be the whole truth or individual silent learning would be
impossible. If you are reading this page alone, is it the
case that you are unable to learn from it because you are not
interacting with others?
 |
Are adults and children all that different? |
Well, it depends on the theory you accept, doesn't it?
It seems clear that concepts such as critical period only apply to children (and the evidence is there to suggest that adult learners have far more trouble learning an additional language than children do). Methodologies which purport, therefore, to be based on how a child learns and that such an approach is applicable to adults and more mature children should be handled with care and some scepticism because there is evidence that children and adults learn differently, not least because of their very different experiential backgrounds and because all normal adults have already acquired a perfect knowledge of their own language.
Other theories, such as Imitation and Reinforcement theories (the
basis of drilling and repetition and much else) as well as Active
Construction of Grammar, Connectionism and Social Interaction theory
may be just as applicable to mature learners of an additional
language as they are to immature learners of first languages.
The argument here is that we do not abandon or lose access to our
cognitive abilities as we mature. We may use the abilities
differently, some might argue more effectively, as adults.
If so, there are obvious consequences for the design of materials,
classroom procedures, error correction techniques and much else.
| Related guides | |
| second-language acquisition | for a guide to some current theories |
| how learning happens | for a fairly simple guide to the area |
| inferencing | for a guide in which there is a little more about how humans use statistical reasoning to understand language |
| noticing | for the guide to techniques for encouraging learners to notice language and to notice differences between their language and what they encounter as models |
| error | for the guide which considers the types and sources of error and the development of interlanguage |
| Krashen and the Natural Approach | for the guide to a very influential idea |
| Chomsky | for the guide to a very influential theorist |
| types of languages | for a guide which sets out the structural ways in which languages differ |
There's a simple matching test on this area.
References and other sources:
An enormous amount of research, some of it focusing very narrowly
on the acquisition of particular structures,
is available to one who looks for it in the discussion of
first-language acquisition. Not all of it is
relevant to ELT.
Aitchison, J, 1989, The Articulate Mammal, London: Unwin
Hyman Ltd.
Bergmann, A, Hall, K & Ross, S (Eds.), 2007, Language files:
Materials for an introduction to language and linguistics,
Columbus, Ohio: The Ohio State University Press
Dennett, D, 2017, From Bacteria to Bach and Back, UK:
Penguin Random House
Ellis, R, 1994, The Study of Second Language Acquisition,
Oxford: Oxford University Press
Todd, L & Hancock, I, 1986, International English Usage,
Beckenham: Croom Helm
